Automation
Since execution of the RUN function can be triggered via a simple function call, there are a number of different automation options available, depending on your specific tools and objectives.
Scheduling
The time of day at which the GA4 BigQuery export arrives is notoriously unpredictable, posing a scheduling challenge: run on a schedule, and risk running before new data has arrived; or deploy infrastructure to trigger the transformation when new data is detected?
Thankfully, we can look at the metadata to help inform the decision. Running this query post-installation on the _partitions metadata table in BigQuery and analysing the results should help identify potential patterns and thresholds.
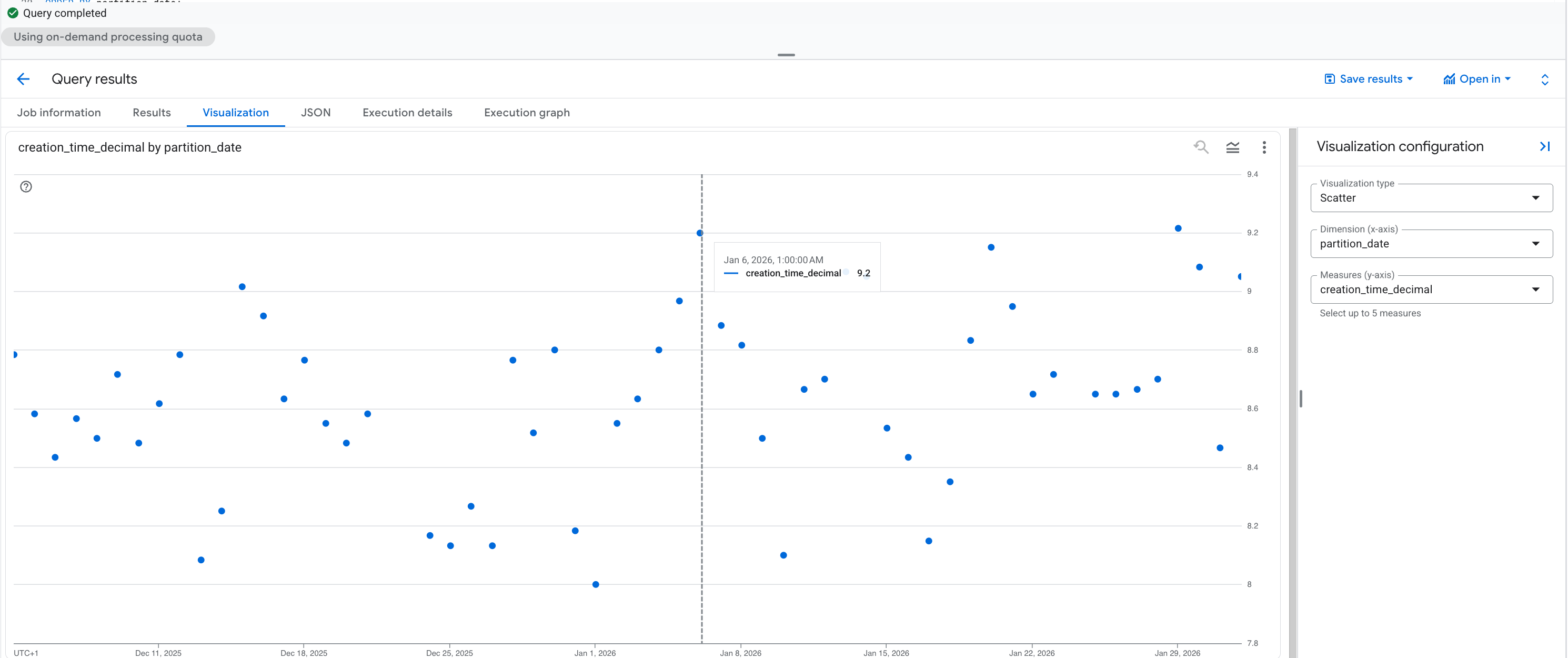
select partition_date, creation_time_decimal
from `[deployment_dataset_id]._partitions`From this scatter plot, it is clear that 100% of all inbound data arrives before 10:00 UTC, so it makes sense to schedule Decode GA4 at this time. However you should run this query on your own metadata to confirm the appropriate scheduling time.
You can also use statistical methods on this metadata to set the timing based on e.g. confidence intervals.
The built-in Vizualisation tab in the Query results pane of BigQuery Studio enables you to quickly inspect the time-series plot on your data, using the following chart configuration on the outputs of the _partitions query:
select partition_date, creation_time_decimal
from `[deployment_dataset_id]._partitions`- Visualization type:
Scatter - Dimension (x-axis):
partition_date - Measures (y-axis):
creation_time_decimal
Tools
Native Scheduling
The simplest scheduling approach is using Scheduled Queries in BigQuery, on a set schedule every day. Since there is no Decode GA4 cost if no data is processed, you can run this multiple times a day to catch late-arriving data.
This could also be triggered via a Cloud Workflow, for enterprise integration with CI/CD pipelines.
Transformation Tools
In order to use the outputs of Decode GA4 in a downstream transformation tool, it is recommended to set the destination_dataset_id option upon installation.
This will result in a segregated dataset containing only the transformed GA4 event data and statistics, to be used as a clean input to the subsequent process.
Executing of the RUN function can then be incorporated into the pre-operations for the tool you are using, which is implemented slightly differently in different tools:
| Tool | Approach |
|---|---|
| dbt | Execute a pre-hook before core model transformations. |
| Dataform | Execute a pre-operation before core model transformations. |
| SQLMesh | Execute a SQL pre_statement before core model transformations (also Python). |
Orchestration Tools
Common orchestration tools permit execution of BigQuery procedures via SQL execution.
| Tool | Approach |
|---|---|
| Airflow | Execute a CALL statement via a BigQueryInsertJobOperator query job configuration. |
| Dagster | Execute a CALL statement using the BigQueryResource from dagster-gcp. |
| Prefect | Execute a CALL statement via the bigquery_query task from prefect-gcp. |
| Kestra | Execute a CALL statement via the BigQuery Query task. |
| Orchestra | Execute a CALL statement via the Run SQL BigQuery task. |
Essentially, any mechanism via which you can execute SQL on BigQuery can be used to trigger Decode GA4.
